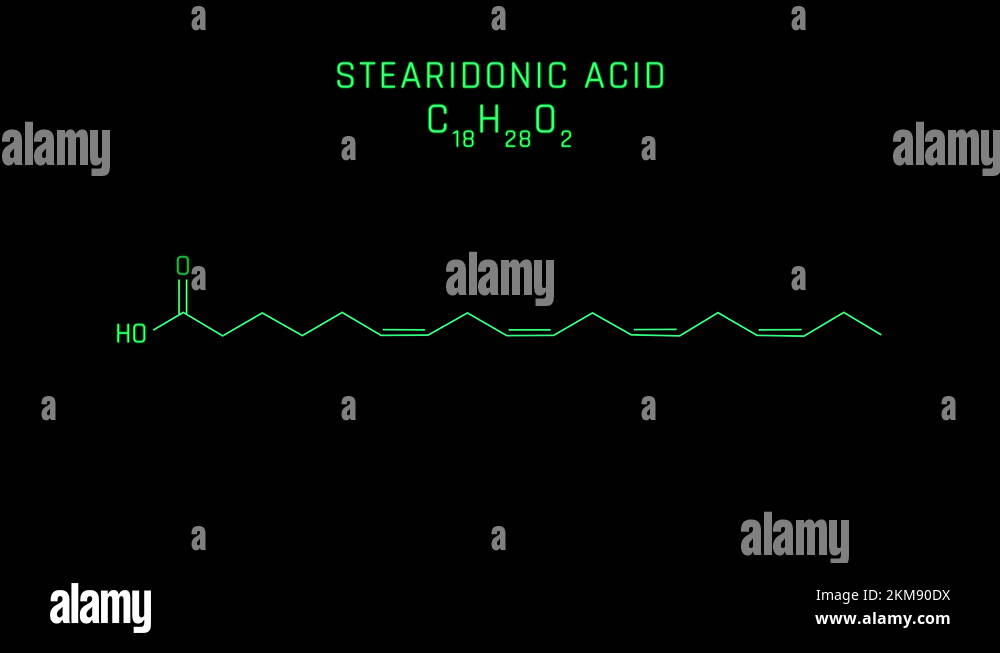
Stearidonic acid (SDA: C18H28O2; 18:4, n-3) is an ω-3 fatty acid, sometimes called moroctic acid.
Biosynthesis
It is biosynthesized from alpha-linolenic acid (ALA: C18H30O2; 18:3, n-3) by the enzyme delta-6-desaturase, which removes two hydrogen (H) atoms.
Stearidonic acid is a precursor to eicosapentaenoic acid.
As it is a precursor to other fatty acids, there has been efforts to enhance the content off stearidonic acid in various crops, such as soybeans.
SDA is also a precursor to N-acylethanolamine (NAEs). Natural sources of this fatty acid are the seed oils of hemp, blackcurrant, corn gromwell, and Echium plantagineum, and the cyanobacterium Spirulina. SDA can also be synthesized in a lab. A GMO soybean source is approved by the European Food Safety Authority.
See also
- List of omega-3 fatty acids
- Omega-3 fatty acids
- Essential fatty acids
References